import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
val spark: SparkSession = ...
scala> spark.catalog
lazy val catalog: org.apache.spark.sql.catalog.Catalog
scala> spark.catalog
res0: org.apache.spark.sql.catalog.Catalog = org.apache.spark.sql.internal.CatalogImpl@1b42eb0f
scala> spark.catalog.listTables.show
+------------------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
| name|database|description|tableType|isTemporary|
+------------------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
|my_permanent_table| default| null| MANAGED| false|
| strs| null| null|TEMPORARY| true|
+------------------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
scala> spark.catalog.clearCacheCatalog
Catalog is the interface to work with a metastore, i.e. a data catalog of database(s), local and external tables, functions, table columns, and temporary views in Spark SQL.
You can access the current catalog using SparkSession.catalog attribute.
The one and only implementation of the Catalog contract is CatalogImpl.
Catalog Contract
package org.apache.spark.sql.catalog
abstract class Catalog {
def currentDatabase: String
def setCurrentDatabase(dbName: String): Unit
def listDatabases(): Dataset[Database]
def listTables(): Dataset[Table]
def listTables(dbName: String): Dataset[Table]
def listFunctions(): Dataset[Function]
def listFunctions(dbName: String): Dataset[Function]
def listColumns(tableName: String): Dataset[Column]
def listColumns(dbName: String, tableName: String): Dataset[Column]
def createExternalTable(tableName: String, path: String): DataFrame
def createExternalTable(tableName: String, path: String, source: String): DataFrame
def createExternalTable(
tableName: String,
source: String,
options: Map[String, String]): DataFrame
def createExternalTable(
tableName: String,
source: String,
schema: StructType,
options: Map[String, String]): DataFrame
def dropTempView(viewName: String): Unit
def isCached(tableName: String): Boolean
def cacheTable(tableName: String): Unit
def uncacheTable(tableName: String): Unit
def clearCache(): Unit
def refreshTable(tableName: String): Unit
def refreshByPath(path: String): Unit
}CatalogImpl
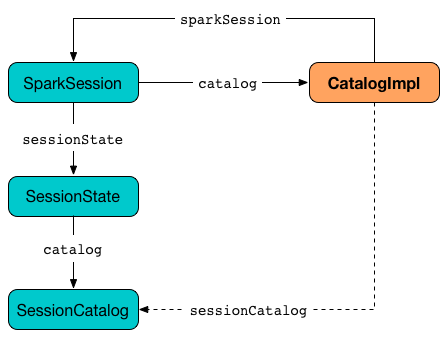
CatalogImpl is the one and only Catalog that relies on a per-session SessionCatalog (through SparkSession) to obey the Catalog contract.
It lives in org.apache.spark.sql.internal package.
Removing All Cached Tables From In-Memory Cache — clearCache Method
clearCache(): UnitclearCache requests CacheManager to remove all cached tables from in-memory cache.
|
Note
|
clearCache is a part of Catalog Contract.
|
Creating External Table From Path — createExternalTable Method
createExternalTable(tableName: String, path: String): DataFrame
createExternalTable(tableName: String, path: String, source: String): DataFrame
createExternalTable(
tableName: String,
source: String,
options: Map[String, String]): DataFrame
createExternalTable(
tableName: String,
source: String,
schema: StructType,
options: Map[String, String]): DataFramecreateExternalTable creates an external table tableName from the given path and returns the corresponding DataFrame.
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
val spark: SparkSession = ...
val readmeTable = spark.catalog.createExternalTable("readme", "README.md", "text")
readmeTable: org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame = [value: string]
scala> spark.catalog.listTables.filter(_.name == "readme").show
+------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
| name|database|description|tableType|isTemporary|
+------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
|readme| default| null| EXTERNAL| false|
+------+--------+-----------+---------+-----------+
scala> sql("select count(*) as count from readme").show(false)
+-----+
|count|
+-----+
|99 |
+-----+The source input parameter is the name of the data source provider for the table, e.g. parquet, json, text. If not specified, createExternalTable uses spark.sql.sources.default setting to know the data source format.
|
Note
|
source input parameter must not be hive as it leads to a AnalysisException.
|
createExternalTable sets the mandatory path option when specified explicitly in the input parameter list.
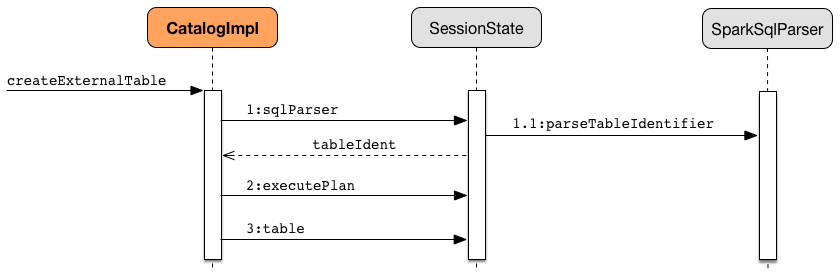
createExternalTable parses tableName into TableIdentifier (using SparkSqlParser). It creates a CatalogTable and then executes (by toRDD) a CreateTable logical plan. The result DataFrame is a Dataset[Row] with the QueryExecution after executing SubqueryAlias logical plan and RowEncoder.