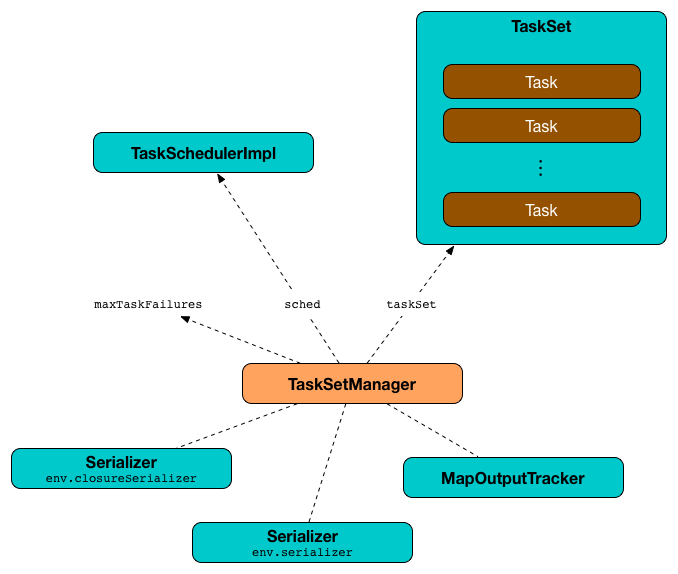
TaskSetManager
TaskSetManager is a Schedulable that manages scheduling of tasks in a TaskSet.
|
Note
|
A TaskSet represents a set of tasks that correspond to missing partitions of a single Stage. |
|
Note
|
A task can end sucessfully or due to a failure (in task execution or an executor being lost). |

When TaskSetManager is created for a TaskSet, TaskSetManager registers all the tasks as pending execution.
The responsibilities of a TaskSetManager include:
|
Tip
|
Enable DEBUG logging levels for A cluster manager is recommended since it gives more task localization choices (with YARN additionally supporting rack localization). |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
The number of the tasks that have already completed execution. Starts from |
|
The number of task copies currently running per task (index in its task set). The number of task copies of a task is increased when dequeuing a task for execution or checking for speculatable tasks and decreased when a task fails or an executor is lost (for a shuffle map stage and no external shuffle service). |
|
Current map output tracker epoch. |
|
Lookup table of TaskInfo’s indices that failed to executor ids and the time of the failure. Used in handleFailedTask. |
|
Disabled, i.e. Read Zombie state in this document. |
|
NOTE: Set immediately when Recomputed every change in the status of executors. |
|
Number of tasks to compute. |
|
Lookup table of task indices per executor. Updated with an task index per executor when |
|
Collection of running tasks that a Used to implement runningTasks (that is simply the size of Used in |
|
The stage’s id a Set when It is a part of Schedulable Contract. |
|
Status of tasks (with a boolean flag, i.e. All tasks start with their flags disabled, i.e. The flag for a task is turned on, i.e. A flag is explicitly turned off only for |
|
Lookup table of A task’s id and NOTE: It appears that the entires stay forever, i.e. are never removed (perhaps because the maintenance overhead is not needed given a |
|
Lookup table of Tasks (per partition id) to schedule execution of. NOTE: The tasks all belong to a single TaskSet that was given when |
|
The current total size of the result of all the tasks that have finished. Starts from Only increased with the size of a task result whenever a |
|
Tip
|
Enable Add the following line to Refer to Logging. |
getLocalityIndex Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
priority Property
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
name Property
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
dequeueSpeculativeTask Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
dequeueTask Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
executorAdded Method
executorAdded simply calls recomputeLocality method.
abortIfCompletelyBlacklisted Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
TaskSetManager is Schedulable
TaskSetManager is a Schedulable with the following implementation:
-
nameisTaskSet_[taskSet.stageId.toString] -
no
parentis ever assigned, i.e. it is alwaysnull.It means that it can only be a leaf in the tree of Schedulables (with Pools being the nodes).
-
schedulingModealways returnsSchedulingMode.NONE(since there is nothing to schedule). -
weightis always1. -
minShareis always0. -
runningTasksis the number of running tasks in the internalrunningTasksSet. -
priorityis the priority of the owned TaskSet (usingtaskSet.priority). -
stageIdis the stage id of the owned TaskSet (usingtaskSet.stageId). -
schedulableQueuereturns no queue, i.e.null. -
addSchedulableandremoveSchedulabledo nothing. -
getSchedulableByNamealways returnsnull. -
getSortedTaskSetQueuereturns a one-element collection with the sole element being itself.
Marking Task As Fetching Indirect Result — handleTaskGettingResult Method
handleTaskGettingResult(tid: Long): UnithandleTaskGettingResult looks the TaskInfo for the task id tid up in taskInfos internal registry and marks it as fetching indirect task result. It then notifies DAGScheduler.
|
Note
|
handleTaskGettingResult is executed when TaskSchedulerImpl is notified about fetching indirect task result.
|
Registering Running Task — addRunningTask Method
addRunningTask(tid: Long): UnitaddRunningTask adds tid to runningTasksSet internal registry and requests the parent pool to increase the number of running tasks (if defined).
Unregistering Running Task — removeRunningTask Method
removeRunningTask(tid: Long): UnitremoveRunningTask removes tid from runningTasksSet internal registry and requests the parent pool to decrease the number of running task (if defined).
Checking Speculatable Tasks — checkSpeculatableTasks Method
|
Note
|
checkSpeculatableTasks is part of the Schedulable Contract.
|
checkSpeculatableTasks(minTimeToSpeculation: Int): BooleancheckSpeculatableTasks checks whether there are speculatable tasks in a TaskSet.
|
Note
|
checkSpeculatableTasks is called when TaskSchedulerImpl checks for speculatable tasks.
|
If the TaskSetManager is zombie or has a single task in TaskSet, it assumes no speculatable tasks.
The method goes on with the assumption of no speculatable tasks by default.
It computes the minimum number of finished tasks for speculation (as spark.speculation.quantile of all the finished tasks).
You should see the DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG Checking for speculative tasks: minFinished = [minFinishedForSpeculation]It then checks whether the number is equal or greater than the number of tasks completed successfully (using tasksSuccessful).
Having done that, it computes the median duration of all the successfully completed tasks (using taskInfos internal registry) and task length threshold using the median duration multiplied by spark.speculation.multiplier that has to be equal or less than 100.
You should see the DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG Task length threshold for speculation: [threshold]For each task (using taskInfos internal registry) that is not marked as successful yet (using successful) for which there is only one copy running (using copiesRunning) and the task takes more time than the calculated threshold, but it was not in speculatableTasks it is assumed speculatable.
You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Marking task [index] in stage [taskSet.id] (on [info.host]) as speculatable because it ran more than [threshold] msThe task gets added to the internal speculatableTasks collection. The method responds positively.
resourceOffer Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME Review TaskSetManager.resourceOffer + Does this have anything related to the following section about scheduling tasks?
|
resourceOffer(
execId: String,
host: String,
maxLocality: TaskLocality): Option[TaskDescription]When a TaskSetManager is a zombie, resourceOffer returns no TaskDescription (i.e. None).
For a non-zombie TaskSetManager, resourceOffer…FIXME
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
It dequeues a pending task from the taskset by checking pending tasks per executor (using pendingTasksForExecutor), host (using pendingTasksForHost), with no localization preferences (using pendingTasksWithNoPrefs), rack (uses TaskSchedulerImpl.getRackForHost that seems to return "non-zero" value for YarnScheduler only)
From TaskSetManager.resourceOffer:
INFO TaskSetManager: Starting task 0.0 in stage 0.0 (TID 0, 192.168.1.4, partition 0,PROCESS_LOCAL, 1997 bytes)If a serialized task is bigger than 100 kB (it is not a configurable value), a WARN message is printed out to the logs (only once per taskset):
WARN TaskSetManager: Stage [task.stageId] contains a task of very large size ([serializedTask.limit / 1024] KB). The maximum recommended task size is 100 KB.A task id is added to runningTasksSet set and parent pool notified (using increaseRunningTasks(1) up the chain of pools).
The following INFO message appears in the logs:
INFO TaskSetManager: Starting task [id] in stage [taskSet.id] (TID [taskId], [host], partition [task.partitionId],[taskLocality], [serializedTask.limit] bytes)For example:
INFO TaskSetManager: Starting task 1.0 in stage 0.0 (TID 1, localhost, partition 1,PROCESS_LOCAL, 2054 bytes)Scheduling Tasks in TaskSet
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
For each submitted TaskSet, a new TaskSetManager is created. The TaskSetManager completely and exclusively owns a TaskSet submitted for execution.
|
Caution
|
FIXME A picture with TaskSetManager owning TaskSet
|
|
Caution
|
FIXME What component knows about TaskSet and TaskSetManager. Isn’t it that TaskSets are created by DAGScheduler while TaskSetManager is used by TaskSchedulerImpl only? |
TaskSetManager keeps track of the tasks pending execution per executor, host, rack or with no locality preferences.
Locality-Aware Scheduling aka Delay Scheduling
TaskSetManager computes locality levels for the TaskSet for delay scheduling. While computing you should see the following DEBUG in the logs:
DEBUG Valid locality levels for [taskSet]: [levels]|
Caution
|
FIXME What’s delay scheduling? |
Recording Successful Task And Notifying DAGScheduler — handleSuccessfulTask Method
handleSuccessfulTask(tid: Long, result: DirectTaskResult[_]): UnithandleSuccessfulTask records the tid task as finished, notifies the DAGScheduler that the task has ended and attempts to mark the TaskSet finished.
|
Note
|
handleSuccessfulTask is executed after TaskSchedulerImpl has been informed that tid task finished successfully (and the task result was deserialized).
|
|
Caution
|
FIXME Describe TaskInfo
|
Internally, handleSuccessfulTask looks TaskInfo up (in taskInfos internal registry) and records it as FINISHED.
It then removes tid task from runningTasksSet internal registry.
handleSuccessfulTask notifies DAGScheduler that tid task ended successfully (with the Task object from tasks internal registry and the result as Success).
At this point, handleSuccessfulTask looks up the other running task attempts of tid task and requests SchedulerBackend to kill them. You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Killing attempt [attemptNumber] for task [id] in stage [id] (TID [id]) on [host] as the attempt [attemptNumber] succeeded on [host]|
Caution
|
FIXME Review taskAttempts
|
If tid has not yet been recorded as successful, handleSuccessfulTask increases tasksSuccessful counter. You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Finished task [id] in stage [id] (TID [taskId]) in [duration] ms on [host] (executor [executorId]) ([tasksSuccessful]/[numTasks])tid task is marked as successful. If the number of task that have finished successfully is exactly the number of the tasks to execute (in the TaskSet), the TaskSetManager becomes a zombie.
If tid task was already recorded as successful, you should merely see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Ignoring task-finished event for [id] in stage [id] because task [index] has already completed successfullyUltimately, handleSuccessfulTask attempts to mark the TaskSet finished.
Attempting to Mark TaskSet Finished — maybeFinishTaskSet Internal Method
maybeFinishTaskSet(): UnitmaybeFinishTaskSet notifies TaskSchedulerImpl that a TaskSet has finished when there are no other running tasks and the TaskSetManager is not in zombie state.
handleFailedTask Method
handleFailedTask(
tid: Long,
state: TaskState,
reason: TaskFailedReason): UnithandleFailedTask removes tid task from the internal registry of running tasks and marks TaskInfo as finished. It decreases the number of the tid task’s copies running (in copiesRunning internal registry).
|
Note
|
handleFailedTask is executed after TaskSchedulerImpl has been informed that tid task failed or executorLost. In either case, tasks could not finish successfully or could not report it back.
|
|
Note
|
With speculative xecution of tasks enabled, there can be many copies of a task running simultaneuosly. |
When executed, handleFailedTask first checks out the status of the tid task. If the tid task has already been marked as failed or killed (in taskInfos internal registry), handleFailedTask does nothing and quits.
If however the task has not been registered as failed or killed before, handleFailedTask unregisters the task as running and marks it as finished with state. The number of the running copies of the task (as recorded in copiesRunning internal registry) is decremented.
|
Caution
|
FIXME How is copiesRunning used?
|
handleFailedTask uses the following pattern as the reason for the failure:
Lost task [id] in stage [taskSetId] (TID [tid], [host], executor [executorId]): [reason]handleFailedTask then calculates the failure exception for the input reason, i.e. FetchFailed, ExceptionFailure, ExecutorLostFailure and other TaskFailedReasons.
|
Note
|
Calculation of the failure exception was moved to their own sections below to make the reading a bit more pleasant and comprehensible. |
handleFailedTask informs DAGScheduler that the tid task has ended (with the Task instance from tasks internal registry, the reason, and no result, i.e. null).
If the tid task has already been marked as successful (in successful internal registry) you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Task [id] in stage [id] (TID [tid]) failed, but another instance of the task has already succeeded, so not re-queuing the task to be re-executed.|
Tip
|
Refer to Speculative Execution of Tasks to learn why a single task could be executed multiple times at the same time. |
If the tid task was not recorded as successful, the task is recorded as a pending task.
Unless the TaskSetManager is a zombie or the task failure should not be counted towards the maximum number of times the task is allowed to fail before the stage is aborted (i.e. TaskFailedReason.countTowardsTaskFailures is enabled), the optional TaskSetBlacklist is updated.
handleFailedTask increments numFailures for tid and makes sure that it is not equal or greater than the allowed number of task failures per TaskSet (as specified when the TaskSetManager was created).
If so, i.e. the number of task failures of tid reached the maximum value, you should see the following ERROR message in the logs:
ERROR Task [id] in stage [id] failed [maxTaskFailures] times; aborting jobAnd handleFailedTask aborts the TaskSet and then quits.
In the end, handleFailedTask attempts to mark the TaskSet as finished.
|
Caution
|
FIXME image with handleFailedTask (and perhaps the other parties involved)
|
FetchFailed TaskFailedReason
For FetchFailed you should see the following WARN message in the logs:
WARN Lost task [id] in stage [id] (TID [tid], [host], executor [id]): [reason]Unless tid has already been marked as successful (in successful internal registry), it becomes so and the number of successful tasks in TaskSet gets increased.
The TaskSetManager enters zombie state.
The failure exception is empty.
ExceptionFailure TaskFailedReason
For ExceptionFailure, handleFailedTask checks if the exception is of type NotSerializableException. If so, you should see the following ERROR message in the logs:
ERROR Task [id] in stage [id] (TID [tid]) had a not serializable result: [description]; not retryingAnd handleFailedTask aborts the TaskSet and then quits.
Otherwise, if the exception is not of type NotSerializableException, handleFailedTask accesses accumulators and calculates whether to print the WARN message (with the failure reason) or the INFO message.
If the failure has already been reported (and is therefore a duplication), spark.logging.exceptionPrintInterval is checked before reprinting the duplicate exception in its entirety.
For full printout of the ExceptionFailure, the following WARN appears in the logs:
WARN Lost task [id] in stage [id] (TID [tid], [host], executor [id]): [reason]Otherwise, the following INFO appears in the logs:
INFO Lost task [id] in stage [id] (TID [tid]) on [host], executor [id]: [className] ([description]) [duplicate [dupCount]]The exception in ExceptionFailure becomes the failure exception.
ExecutorLostFailure TaskFailedReason
For ExecutorLostFailure if not exitCausedByApp, you should see the following INFO in the logs:
INFO Task [tid] failed because while it was being computed, its executor exited for a reason unrelated to the task. Not counting this failure towards the maximum number of failures for the task.The failure exception is empty.
Task retries and spark.task.maxFailures
When you start Spark program you set up spark.task.maxFailures for the number of failures that are acceptable until TaskSetManager gives up and marks a job failed.
|
Tip
|
In Spark shell with local master, spark.task.maxFailures is fixed to 1 and you need to use local-with-retries master to change it to some other value.
|
In the following example, you are going to execute a job with two partitions and keep one failing at all times (by throwing an exception). The aim is to learn the behavior of retrying task execution in a stage in TaskSet. You will only look at a single task execution, namely 0.0.
$ ./bin/spark-shell --master "local[*, 5]"
...
scala> sc.textFile("README.md", 2).mapPartitionsWithIndex((idx, it) => if (idx == 0) throw new Exception("Partition 2 marked failed") else it).count
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO DAGScheduler: Submitting 2 missing tasks from ResultStage 1 (MapPartitionsRDD[7] at mapPartitionsWithIndex at <console>:25)
15/10/27 17:24:56 DEBUG DAGScheduler: New pending partitions: Set(0, 1)
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSchedulerImpl: Adding task set 1.0 with 2 tasks
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSetManager: Starting task 0.0 in stage 1.0 (TID 2, localhost, partition 0,PROCESS_LOCAL, 2062 bytes)
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO Executor: Running task 0.0 in stage 1.0 (TID 2)
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 ERROR Executor: Exception in task 0.0 in stage 1.0 (TID 2)
java.lang.Exception: Partition 2 marked failed
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSetManager: Starting task 0.1 in stage 1.0 (TID 4, localhost, partition 0,PROCESS_LOCAL, 2062 bytes)
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO Executor: Running task 0.1 in stage 1.0 (TID 4)
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO HadoopRDD: Input split: file:/Users/jacek/dev/oss/spark/README.md:0+1784
15/10/27 17:24:56 ERROR Executor: Exception in task 0.1 in stage 1.0 (TID 4)
java.lang.Exception: Partition 2 marked failed
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 ERROR Executor: Exception in task 0.4 in stage 1.0 (TID 7)
java.lang.Exception: Partition 2 marked failed
...
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSetManager: Lost task 0.4 in stage 1.0 (TID 7) on executor localhost: java.lang.Exception (Partition 2 marked failed) [duplicate 4]
15/10/27 17:24:56 ERROR TaskSetManager: Task 0 in stage 1.0 failed 5 times; aborting job
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSchedulerImpl: Removed TaskSet 1.0, whose tasks have all completed, from pool
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO TaskSchedulerImpl: Cancelling stage 1
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO DAGScheduler: ResultStage 1 (count at <console>:25) failed in 0.058 s
15/10/27 17:24:56 DEBUG DAGScheduler: After removal of stage 1, remaining stages = 0
15/10/27 17:24:56 INFO DAGScheduler: Job 1 failed: count at <console>:25, took 0.085810 s
org.apache.spark.SparkException: Job aborted due to stage failure: Task 0 in stage 1.0 failed 5 times, most recent failure: Lost task 0.4 in stage 1.0 (TID 7, localhost): java.lang.Exception: Partition 2 marked failedZombie state
A TaskSetManager is in zombie state when all tasks in a taskset have completed successfully (regardless of the number of task attempts), or if the taskset has been aborted.
While in zombie state, a TaskSetManager can launch no new tasks and responds with no TaskDescription to resourceOffers.
A TaskSetManager remains in the zombie state until all tasks have finished running, i.e. to continue to track and account for the running tasks.
Aborting TaskSet — abort Method
abort(message: String, exception: Option[Throwable] = None): Unitabort informs DAGScheduler that the TaskSet has been aborted.
|
Caution
|
FIXME image with DAGScheduler call |
The TaskSetManager enters zombie state.
Finally, abort attempts to mark the TaskSet finished.
Checking Available Memory For Task Result — canFetchMoreResults Method
canFetchMoreResults(size: Long): BooleancanFetchMoreResults checks whether there is enough memory to fetch the result of a task.
Internally, canFetchMoreResults increments the internal totalResultSize with the input size which is the result of a task. It also increments the internal calculatedTasks.
If the current internal totalResultSize is bigger than spark.driver.maxResultSize the following ERROR message is printed out to the logs:
ERROR TaskSetManager: Total size of serialized results of [calculatedTasks] tasks ([totalResultSize]) is bigger than spark.driver.maxResultSize ([maxResultSize])Otherwise, canFetchMoreResults returns true.
|
Note
|
canFetchMoreResults is used in TaskResultGetter.enqueueSuccessfulTask only.
|
Creating TaskSetManager Instance
TaskSetManager takes the following when created:
-
TaskSet that the
TaskSetManagermanages scheduling for
TaskSetManager initializes the internal registries and counters.
TaskSetManager requests the current epoch from MapOutputTracker and sets it on all tasks in the taskset.
|
Note
|
TaskSetManager uses TaskSchedulerImpl (that was given when created) to access the current MapOutputTracker.
|
You should see the following DEBUG in the logs:
DEBUG Epoch for [taskSet]: [epoch]|
Caution
|
FIXME Why is the epoch important? |
|
Note
|
TaskSetManager requests MapOutputTracker from TaskSchedulerImpl which is likely for unit testing only since MapOutputTracker is available using SparkEnv.
|
TaskSetManager adds the tasks as pending execution (in reverse order from the highest partition to the lowest).
|
Caution
|
FIXME Why is reverse order important? The code says it’s to execute tasks with low indices first. |
Registering Task As Pending Execution (Per Preferred Locations) — addPendingTask Internal Method
addPendingTask(index: Int): UnitaddPendingTask registers a index task in the pending-task lists that the task should be eventually scheduled to (per its preferred locations).
Internally, addPendingTask takes the preferred locations of the task (given index) and registers the task in the internal pending-task registries for every preferred location:
-
pendingTasksForExecutor when the
TaskLocationisExecutorCacheTaskLocation. -
pendingTasksForHost for the hosts of a
TaskLocation. -
pendingTasksForRack for the racks from
TaskSchedulerImplper the host (of aTaskLocation).
For a TaskLocation being HDFSCacheTaskLocation, addPendingTask requests TaskSchedulerImpl for the executors on the host (of a preferred location) and registers the task in pendingTasksForExecutor for every executor (if available).
You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Pending task [index] has a cached location at [host] , where there are executors [executors]When addPendingTask could not find executors for a HDFSCacheTaskLocation preferred location, you should see the following DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG Pending task [index] has a cached location at [host] , but there are no executors alive there.If the task has no location preferences, addPendingTask registers it in pendingTasksWithNoPrefs.
addPendingTask always registers the task in allPendingTasks.
|
Note
|
addPendingTask is used immediatelly when TaskSetManager is created and later when handling a task failure or lost executor.
|
Re-enqueuing ShuffleMapTasks (with no ExternalShuffleService) and Reporting All Running Tasks on Lost Executor as Failed — executorLost Method
executorLost(execId: String, host: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): UnitexecutorLost re-enqueues all the ShuffleMapTasks that have completed already on the lost executor (when external shuffle service is not in use) and reports all currently-running tasks on the lost executor as failed.
|
Note
|
executorLost is a part of the Schedulable contract that TaskSchedulerImpl uses to inform TaskSetManagers about lost executors.
|
|
Note
|
Since TaskSetManager manages execution of the tasks in a single TaskSet, when an executor gets lost, the affected tasks that have been running on the failed executor need to be re-enqueued. executorLost is the mechanism to "announce" the event to all TaskSetManagers.
|
Internally, executorLost first checks whether the tasks are ShuffleMapTasks and whether an external shuffle service is enabled (that could serve the map shuffle outputs in case of failure).
|
Note
|
executorLost checks out the first task in tasks as it is assumed the other belong to the same stage. If the task is a ShuffleMapTask, the entire TaskSet is for a ShuffleMapStage.
|
|
Note
|
executorLost uses SparkEnv to access the current BlockManager and finds out whether an external shuffle service is enabled or not (that is controlled using spark.shuffle.service.enabled property).
|
If executorLost is indeed due to an executor lost that executed tasks for a ShuffleMapStage (that this TaskSetManager manages) and no external shuffle server is enabled, executorLost finds all the tasks that were scheduled on this lost executor and marks the ones that were already successfully completed as not executed yet.
|
Note
|
executorLost uses records every tasks on the lost executor in successful (as false) and decrements [copiesRunning copiesRunning], and tasksSuccessful for every task.
|
executorLost registers every task as pending execution (per preferred locations) and informs DAGScheduler that the tasks (on the lost executor) have ended (with Resubmitted reason).
|
Note
|
executorLost uses TaskSchedulerImpl to access the DAGScheduler. TaskSchedulerImpl is given when the TaskSetManager was created.
|
Regardless of whether this TaskSetManager manages ShuffleMapTasks or not (it could also manage ResultTasks) and whether the external shuffle service is used or not, executorLost finds all currently-running tasks on this lost executor and reports them as failed (with the task state FAILED).
|
Note
|
executorLost finds out if the reason for the executor lost is due to application fault, i.e. assumes ExecutorExited's exit status as the indicator, ExecutorKilled for non-application’s fault and any other reason is an application fault.
|
executorLost recomputes locality preferences.
Recomputing Task Locality Preferences — recomputeLocality Method
recomputeLocality(): UnitrecomputeLocality recomputes the internal caches: myLocalityLevels, localityWaits and currentLocalityIndex.
|
Caution
|
FIXME But why are the caches important (and have to be recomputed)? |
recomputeLocality records the current TaskLocality level of this TaskSetManager (that is currentLocalityIndex in myLocalityLevels).
|
Note
|
TaskLocality is one of PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL, NO_PREF, RACK_LOCAL and ANY values.
|
recomputeLocality computes locality levels (for scheduled tasks) and saves the result in myLocalityLevels internal cache.
recomputeLocality computes localityWaits (by finding locality wait for every locality level in myLocalityLevels internal cache).
In the end, recomputeLocality getLocalityIndex of the previous locality level and records it in currentLocalityIndex.
Computing Locality Levels (for Scheduled Tasks) — computeValidLocalityLevels Internal Method
computeValidLocalityLevels(): Array[TaskLocality]computeValidLocalityLevels computes valid locality levels for tasks that were registered in corresponding registries per locality level.
|
Note
|
TaskLocality is a task locality preference and can be the most localized NODE_LOCAL through NO_PREF and RACK_LOCAL to ANY.
|
| TaskLocality | Internal Registry |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
computeValidLocalityLevels walks over every internal registry and if it is not empty computes locality wait for the corresponding TaskLocality and proceeds with it only when the locality wait is not 0.
For TaskLocality with pending tasks, computeValidLocalityLevels asks TaskSchedulerImpl whether there is at least one executor alive (for PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL and RACK_LOCAL) and if so registers the TaskLocality.
|
Note
|
computeValidLocalityLevels uses TaskSchedulerImpl that was given when TaskSetManager was created.
|
computeValidLocalityLevels always registers ANY task locality level.
In the end, you should see the following DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG TaskSetManager: Valid locality levels for [taskSet]: [comma-separated levels]|
Note
|
computeValidLocalityLevels is used when TaskSetManager is created and later to recompute locality.
|
Finding Locality Wait — getLocalityWait Internal Method
getLocalityWait(level: TaskLocality): LonggetLocalityWait finds locality wait (in milliseconds) for a given TaskLocality.
getLocalityWait uses spark.locality.wait (default: 3s) when the TaskLocality-specific property is not defined or 0 for NO_PREF and ANY.
|
Note
|
NO_PREF and ANY task localities have no locality wait.
|
| TaskLocality | Spark Property |
|---|---|
PROCESS_LOCAL |
|
NODE_LOCAL |
|
RACK_LOCAL |
|
Note
|
getLocalityWait is used when TaskSetManager calculates localityWaits, computes locality levels (for scheduled tasks) and recomputes locality preferences.
|
Settings
| Spark Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
The maximum size of all the task results in a Used when |
|
|
|
Time interval to pass after which a task can be re-launched on the executor where it has once failed. It is to prevent repeated task failures due to executor failures. |
|
How frequently to reprint duplicate exceptions in full (in millis). |
|
|
For locality-aware delay scheduling for |
|
The value of spark.locality.wait |
Scheduling delay for |
|
The value of spark.locality.wait |
Scheduling delay for |
|
The value of spark.locality.wait |
Scheduling delay for |